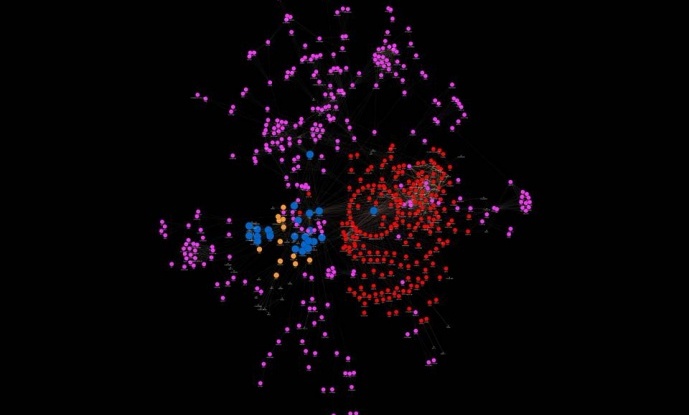
SUMO Gene Network
Protein post-translational modifications (PTMs) diversify the proteome and install new regulatory levels that are crucial for the maintenance of cellular homeostasis. The ubiquitin-like modifying peptide SUMO has been shown to regulate various nuclear processes, including transcriptional control. In plants, the sumoylation pathway has been significantly implicated in development, the response to environmental stimuli, modulation of ABA and other hormones, and nutrient homeostasis. This PTM is a stepwise enzymatic process comprising E1 activation, E2 conjugation, and E3 ligation, mediating the covalent attachment of SUMO peptides to target proteins. The deconjugation process recycles SUMO by action of ubiquitin-like proteases (ULPs) with isopeptidase activity, acting also as endopeptidases of the pre-SUMO peptide.
Plant sumoylation research has seen significant advances in recent years, particularly since high-throughput proteomics strategies have enabled the discovery of hundreds of potential SUMO targets and interactors of SUMO pathway components. The present resource compiles the SUMO Gene Network (SGN), a curated assembly of Arabidopsis thaliana genes that have been functionally associated with sumoylation, from SUMO pathway components to targets and interactors.
To download the SUMO Gene Network v1 [Jul 2015] click here.